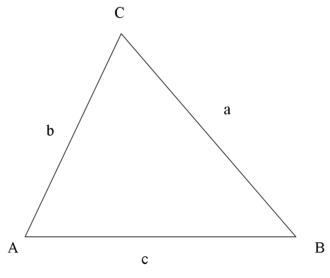
In the following identities, $A,\;B,\;C\;$ are the angles of a triangle and $a,\;b,\;c\;$ are lenghts of sides of the triangle opposite the respective angles (as shown in the diagram).
1. Mathematics Magazine, 97:1 (2024) Problems and Solutions, p. 82, Quiquie 1138
$$a^2 \cdot sin (B-C)=(b^2-c^2) \cdot sinA.$$
Niciun comentariu:
Trimiteți un comentariu